Inscriptions now represent a small fraction of transactions on leading Ethereum L2s
The surging activity surrounding inscription protocols on networks supporting Ethereum Virtual Machine smart contracts has died down from an initial frenzy just a couple of weeks ago.
Data from Dune Analytics shows that inscriptions continue to represent an outsized share of activity on Avalanche and Ethereum’s Goerli testnet, but have since died down on leading Layer 2 networks in addition to the Polygon PoS sidechain and BNB Chain.
Over the past seven days, inscriptions accounted for 77% of transactions on Avalanche, 67% on Goerli, 10% on Base, 7.5% on ZkSync Era, less than 5% on BNB Chain and OP Mainnet, and just 1% on Polygon PoS Chain.
For comparison, inscriptions made up between 50% and 75% of transactions executed on Gnosis, Arbitrum, and ZkSync Era, and more than 40% on BNB Chain and Polygon PoS Chain in mid-December.
Further, more than 77% of Avalanche’s weekly network transaction fees were spent on inscriptions roughly three weeks ago, with 39% of gas spent on ZkSync Era, 18% on Arbitrum, 16% on Gnosis, and 13% on BNB Chain also funding inscription transactions at the time.
That figure has since dropped to 28% on Avalanche, 3.5% on ZkSync Era, and less than 1% of fees spent on Arbitrum, Gnosis, and BNB Chain.
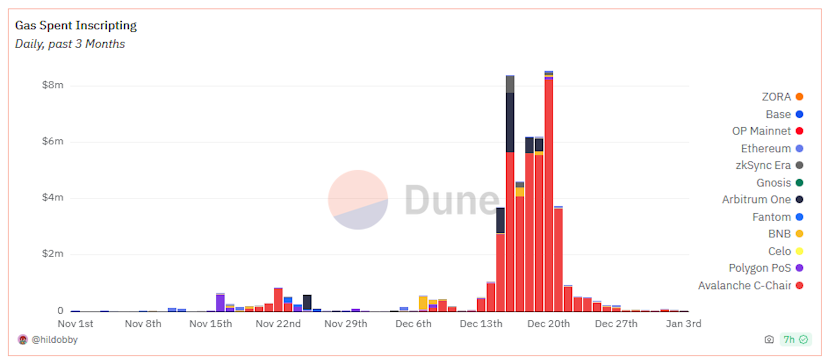
The decline in inscription activity follows an initial surge as inscription protocols proliferated across EVM-compatible chains in recent weeks.
Inscriptions were invented in January as a coding technique for creating pseudo-NFTs on Bitcoin, which does not support the smart contract functionality typically used to create non-fungible tokens on EVM chains. The tokens are created by inscribing data to the smallest denomination of a network token (i.e. a single Bitcoin satoshi), meaning inscriptions are less gas-intensive than NFTs, which require smart contract executions.
Transaction fees on Near, Polygon, and Fantom rocketed 4,500%, 6,900%, and nearly 9,000% respectively amid a flurry of activity following the launch of native inscription protocols in late November.
The throughput of several Layer 2 networks were also pushed to unprecedented highs as inscription protocols rolled out. Arbitrum and ZkSync Era each hosted roughly 60 transactions per second on average on Dec. 16, beating out their previous respective highs by double and quadruple, according to L2beat.
However, the lack of EVM-compatibility means inscription tokens are not composable with third-party protocols, meaning they have no utility within the context of DeFi beyond simple speculation. Inscription tokens also necessitate off-chain indexing.
Credit: Source link




